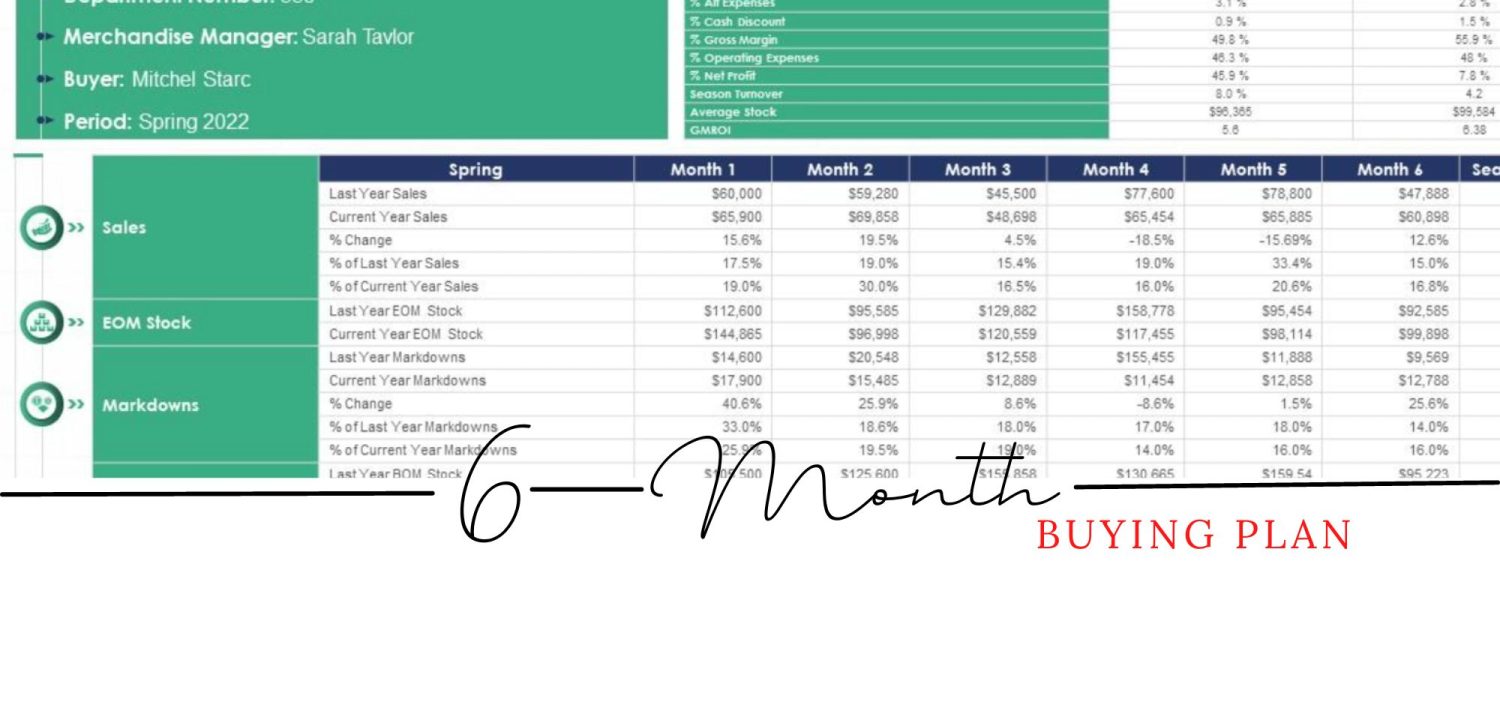
6 month buying plan
A 6 month buying plan is a strategy that helps you organize and manage your spending over a 6-month period. It involves identifying your financial goals, determining your expenses, and creating a budget to ensure you are able to meet those goals without going overboard.
Creating a 6 month buying plan involves several steps:
- Set your financial goals: The first step in creating a 6 month buying plan is to determine your financial goals. This could include saving for a down payment on a house, paying off debt, building an emergency fund, or any other financial goal you have in mind.
- Track your expenses: To create an effective 6 month buying plan, you need to know where your money is going. Start by tracking your expenses for a month or two to get a clear picture of your spending habits. This will help you identify areas where you may be overspending and where you can cut back.
- Create a budget: Once you have a clear picture of your expenses, it’s time to create a budget. Start by listing all of your fixed expenses (rent, utilities, car payment, etc.) and then list your variable expenses (groceries, entertainment, clothing, etc.). Be sure to allocate money for your financial goals as well.
- Stick to your budget: Creating a budget is one thing, but sticking to it is another. To ensure you stay on track, you may need to make some sacrifices or cut back on certain expenses. It’s important to remember your financial goals and keep them in mind when making purchasing decisions.
- Review and adjust: Your 6 month buying plan is not set in stone. It’s important to review your budget regularly to ensure you are staying on track and make adjustments as needed.
Benefits of a 6 month buying plan:
- Helps you achieve financial goals: By creating a 6 month buying plan, you are able to identify your financial goals and create a plan to achieve them.
- Reduces stress: A 6 month buying plan can help you reduce financial stress by giving you a clear picture of your financial situation and helping you stay on track.
- Helps you save money: By tracking your expenses and creating a budget, you can identify areas where you can cut back on expenses and save money.
- Improves financial literacy: Creating a 6 month buying plan can help improve your financial literacy by giving you a better understanding of your finances and how to manage them effectively.
A 6 month buying plan is a valuable tool for anyone looking to improve their financial situation. By setting financial goals, tracking expenses, creating a budget, sticking to it, and reviewing and adjusting regularly, you can take control of your finances and achieve your financial goals.
Initial Markup
Retailers use different pricing strategies to maximize profits and increase sales. One such strategy is the use of initial markup, which refers to the difference between the cost of goods and the initial selling price. The initial markup percentage is calculated by dividing the difference between the selling price and the cost by the cost and multiplying by 100.
Initial markup is an important pricing tool that retailers use to determine the price of their products. It is used to cover the costs associated with buying, storing, and displaying products, as well as to generate profit. Retailers must strike a balance between setting a price that is high enough to cover costs and generate profits, but not so high that it discourages customers from making a purchase.
The initial markup percentage varies depending on the industry and the product being sold. For example, luxury goods typically have a higher initial markup percentage than everyday items like groceries. Retailers may also adjust the initial markup percentage based on the season, the competition, and other factors.
One of the benefits of using initial markup is that it allows retailers to set a consistent pricing structure across different product categories. For example, a retailer may set an initial markup of 50% for all products in a particular category, such as clothing. This ensures that the retailer is making a consistent profit on all products in that category, regardless of their individual costs.
Another benefit of using initial markup is that it provides a cushion for retailers in case of unexpected costs or changes in the market. If a product’s cost increases unexpectedly, the retailer can adjust the selling price to maintain their desired initial markup percentage. Additionally, if a product is not selling well, the retailer can adjust the price to reduce the initial markup percentage and encourage sales.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to using initial markup. For example, if a retailer sets the initial markup percentage too high, it may discourage customers from making a purchase. Similarly, if the initial markup percentage is too low, the retailer may not generate enough profit to cover their costs.
Therefore, an initial markup is a pricing strategy that retailers use to set the initial selling price of their products. It is an important tool that helps retailers cover their costs and generate profits. While there are potential drawbacks to using initial markup, it can be an effective pricing strategy when used appropriately.
How to Create a 6 Month Buying Plan
Creating a buying plan can be an excellent way to manage your finances and make sure that you have the money you need to purchase the things you want. A 6-month buying plan can be especially useful as it allows you to plan for the immediate future while still giving you enough time to adjust your spending habits and make any necessary changes. Here’s how you can create a 6-month buying plan.
Step 1: Assess Your Finances
The first step to creating a 6-month buying plan is to assess your current financial situation. Take a look at your income, expenses, debts, and savings to get a clear picture of where you stand. This will help you determine how much money you have available to spend on purchases and how much you can save for the future.
Step 2: Identify Your Priorities
The next step is to identify your priorities. Make a list of the things you want or need to purchase over the next 6 months, and rank them in order of importance. This could include anything from a new laptop or phone to a vacation or home renovation project. Knowing what you want to buy will help you prioritize your spending and allocate your funds accordingly.
Step 3: Set a Budget
Once you know what you want to buy, it’s time to set a budget. Start by allocating a certain amount of money to each item on your list, based on your priorities. Be realistic about what you can afford and make sure to leave some wiggle room for unexpected expenses.
Step 4: Plan for Savings
Along with setting a budget for your purchases, it’s important to plan for savings. Determine how much money you want to save over the next 6 months and set a goal for yourself. Consider setting up automatic savings transfers or using a budgeting app to help you stay on track.
Step 5: Monitor Your Progress
As you work through your 6-month buying plan, it’s important to monitor your progress. Keep track of your spending and savings to ensure that you’re on track to meet your goals. If you find that you’re falling behind, consider adjusting your budget or making changes to your spending habits.
Step 6: Review and Adjust
Finally, at the end of the 6-month period, review your buying plan and assess your progress. Did you meet your goals? Were there any unexpected expenses or changes that impacted your plan? Use this information to adjust your plan for the future and continue working toward your financial goals.
In conclusion, creating a 6-month buying plan can be a great way to manage your finances and make sure that you have the money you need to purchase the things you want. By assessing your finances, identifying your priorities, setting a budget, planning for savings, monitoring your progress, and reviewing and adjusting your plan, you can set yourself up for financial success in the months ahead.
6 Month Merchandise Plan Excel Template
Here is an example Excel spreadsheet that can be used to create a 6-month buying plan for a retail business:
| Product Category | Product Name | COGS | Initial Markup | Selling Price | Lead Time (weeks) | Forecasted Sales per week | Inventory Needed per Week | Order Quantity | Order Frequency |
| Shorts | Women’s Shorts | $10 | 50% | $15 | 4 | 50 | 200 | 800 | Every 4 weeks |
| Men’s Shorts | $12 | 50% | $18 | 4 | 30 | 120 | 480 | Every 4 weeks | |
| T-Shirts | Women’s T-Shirts | $8 | 50% | $12 | 4 | 75 | 300 | 1200 | Every 4 weeks |
| Men’s T-Shirts | $10 | 50% | $15 | 4 | 50 | 200 | 800 | Every 4 weeks | |
| Dresses | Women’s Dresses | $20 | 50% | $30 | 4 | 20 | 80 | 320 | Every 4 weeks |
| Accessories | Sunglasses | $5 | 50% | $7.50 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 80 | Every 2 weeks |
| Hats | $7 | 50% | $10.50 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 80 | Every 2 weeks |
In this example, the spreadsheet includes columns for the product category, product name, cost of goods sold (COGS), initial markup, selling price, lead time, forecasted sales per week, inventory needed per week, order quantity, and order frequency.
The lead time column indicates how many weeks it takes for the products to be delivered after an order is placed. The forecasted sales per week column is based on sales data and market trends, and is used to calculate the inventory needed per week.
The order quantity and order frequency columns are used to determine how much inventory to order and how often to place orders. In this example, the store owner plans to order inventory every 4 weeks for most products, but orders accessories every 2 weeks due to the shorter lead time.
By using this Excel spreadsheet to create a 6-month buying plan, the store owner can easily track inventory levels, monitor sales data, and adjust inventory levels as needed to ensure that the business is well-stocked and profitable.
Inventory Planning and Retail Buying Plan
Let’s use an example of a clothing store to create a 6-month buying plan.
Step 1: Analyze Sales Data
The first step is to analyze sales data to identify trends and patterns in customer demand. The clothing store has been in operation for several years, so there is a lot of data available to analyze.
After reviewing the data, the store owner notices that there is a significant increase in sales during the summer months. This is likely due to the warmer weather and increased foot traffic in the shopping area. Based on this data, the store owner decides to increase inventory levels during the summer months.
Step 2: Consider Lead Time
The next step is to consider lead time when planning inventory levels. The store owner contacts suppliers and learns that it takes 2 weeks to receive inventory once an order is placed. Based on this lead time, the store owner needs to place orders 2 weeks in advance to ensure that inventory is available when needed.
Step 3: Determine Initial Markup
The store owner wants to maintain a consistent initial markup of 50% on all products. To determine the selling price of each product, the store owner calculates the cost of goods sold (COGS) and adds 50% to the COGS. For example, if the COGS for a shirt is $20, the selling price would be $30.
Step 4: Select Products to Stock
Based on sales data and market trends, the store owner decides to focus on summer clothing for the next 6 months. This includes items such as shorts, t-shirts, and dresses. The store owner also decides to carry a small selection of accessories, such as sunglasses and hats, to complement the summer clothing.
Step 5: Negotiate Prices
The store owner contacts suppliers and negotiates prices for the selected products. After some negotiation, the store owner is able to secure a 10% discount on all orders over $1,000.
Step 6: Determine Inventory Levels
Using the sales data and lead time information, the store owner determines the inventory levels needed for the next 6 months. The store owner decides to order inventory every 4 weeks to ensure that inventory levels are maintained throughout the 6-month period.
For example, the store owner calculates that they will sell 50 pairs of shorts per week during the summer months. With a 4-week lead time, the store owner needs to order 200 pairs of shorts every 4 weeks to maintain inventory levels.
Step 7: Monitor Inventory Levels
Throughout the 6-month period, the store owner closely monitors inventory levels to ensure that they are maintaining the appropriate levels. The store owner tracks sales data and adjusts inventory levels as needed to ensure that they always have enough inventory to meet demand.
Conclusion
Creating a 6-month buying plan is a critical step for any retail business. By analyzing sales data, considering lead time, determining initial markup, selecting products to stock, negotiating prices, and monitoring inventory levels, you can ensure that your business has enough inventory to meet demand while minimizing costs. With a well-executed buying plan, your retail business can increase profits and thrive in a competitive market.